identity management (ID management)
What is identity management (ID management)?
Identity management (ID management) is the organizational process for ensuring individuals have the appropriate access to technology resources.
This includes the identification, authentication and authorization of a person, or persons, to have access to applications, systems or networks. This is done by associating user rights and restrictions with established identities.
Managed identities can also refer to software processes that need access to organizational systems. Identity management is an essential component of security.
Identity management includes authenticating users and determining whether they're allowed access to particular systems. ID management works hand in hand with identity and access management (IAM) systems. Identity management is focused on authentication, while access management is aimed at authorization.
Importance of identity management
The main goal of identity management is to ensure only authenticated users are granted access to the specific applications, systems or IT environments for which they are authorized. This includes control over user provisioning and the process of onboarding new users, such as employees, partners, clients and other stakeholders.
Identity management also includes control over the process of authorizing system or network permissions for existing users and offboarding users who are no longer authorized to access organizational systems.
ID management determines whether a user has access to systems and sets the level of access and permissions a user has on a particular system. For instance, a user might be authorized to access a system but be restricted from some of its components.
Identity governance -- the policies and processes that guide how roles and user access are administered across a business environment -- is an important aspect of identity management. Identity governance is key to successfully managing role-based access management systems.
ID management security benefits
Identity management is an important part of the enterprise security plan because it is linked to both the security and productivity of the organization.
In many organizations, users are granted more access privileges than they need to perform their functions -- known as privilege creep. Attackers can take advantage of compromised user credentials to gain access to an organization's network and data. Using identity management, organizations can safeguard their corporate assets against many threats including hacking, ransomware, phishing and other malware attacks.
Identity management systems add a layer of protection by ensuring user access policies and rules are applied consistently across an organization.
What are IAM systems?
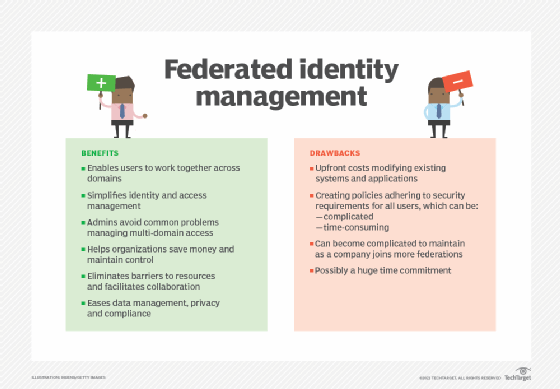
An IAM system provides a framework with the policies and technology needed to support the management of identities. Many of today's IAM systems use federated identity, which allows a single digital identity to be authenticated and stored across multiple different systems.

An IAM system can also deploy single sign-on (SSO) technologies. This can significantly decrease the number of passwords users need to remember. SSO incorporates a federated identity approach by using a single login and password to create an authentication token, which can then be accepted by various enterprise systems and applications.
Combined with multifactor authentication and enforceable security policies, enterprises can lower the risk of security breaches. An example of such policies includes the principle of least privilege, which gives users only the access they require to fulfill their roles.
Identity management implementation challenges
To implement identity management, enterprises must plan and collaborate across business units. Successful organizations are those that establish identity management strategies with clear objectives, have defined business processes and get buy-in from stakeholders at the outset. Identity management works best when IT, security, HR and other departments are involved.
Identity management systems must enable companies to automatically manage multiple users in different situations and computing environments in real time. It's time-consuming to manually adjust access privileges and access controls for hundreds or thousands of users. Authentication must also be simple for users to perform and easy for IT to deploy and secure.
One of the top challenges in implementing identity management is password management. IT professionals should invest in techniques that reduce the impact of password issues in their companies.
Identity management tools should run as applications on a dedicated network appliance or server. At the core of an identity management system are policies defining which devices and users are allowed on the network and what a user can accomplish, depending on device type, location and other factors.
Management console functionality is key. It should include policy definition, reporting, alerts, alarms and other common management and operations requirements. An alert might be triggered, for example, when a specific user tries to access a resource to which they do not have permission. Reporting produces an audit log documenting what specific activities were initiated.
Many identity management systems offer directory integration, support for wired and wireless users, and the flexibility to meet almost any security and operational policy requirement.
Because bring your own device is so strategic today, time-saving features, support for a variety of mobile operating systems and automated device status verification are now common. Time-saving features include automated device onboarding and provisioning.
Identity management benefits
In addition to managing employees, use of identity management along with access management enables businesses to manage customer, partner, supplier and device access to their systems while ensuring security.
This can be accomplished on several fronts, starting with allowing authorized access from anywhere. As people increasingly use social media identities to access services and resources, organizations must be able to reach their users through any platform. Additionally, they can allow users access to corporate systems through their existing digital identities.
Identity management can also improve employee productivity. This is especially important when onboarding new employees or changing authorizations for accessing different systems when an employee's function changes.
When companies hire new employees, they have to be given access to specific parts of their systems, given new devices and provisioned into the business. Done manually, this process can be time-consuming and reduces the ability of the employees to start working. However, automated provisioning can enable companies to accelerate the process of allowing new employees to access the required parts of their systems.
Identity management can also be an important tool for enhancing employee user experience, especially to reduce the impact of identity chaos -- the state of having multiple sets of user IDs and passwords for disparate systems. People typically can't remember multiple usernames and passwords and would prefer to use a single identity to log in to different systems at work. SSO and unified identities enable customers and other stakeholders to access different areas of an enterprise system with one account, ensuring a seamless user experience.
Editor's note: TechTarget editors revised this article in 2024 to improve the reader experience.







