greenfield deployment
What is greenfield deployment?
A greenfield deployment is the design, installation and configuration of computer infrastructure where none existed before, for example, in a new office. In contrast, a brownfield deployment is an upgrade or addition to existing infrastructure using legacy components.
Greenfield deployments are also called greenfield projects. They can be a computer network, website, software package, cloud software, telecom or data center installations that don't use previously developed infrastructure. The terms greenfield and brownfield come from construction, with greenfield being new, undeveloped grassland and brownfield being land that is already built on.
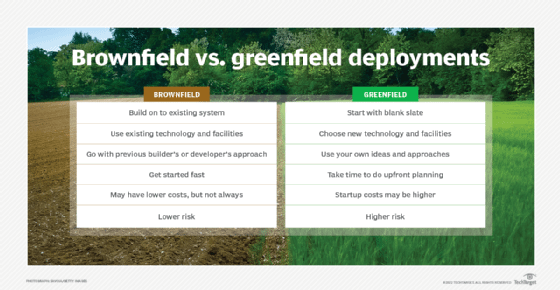
When to consider greenfield deployment strategies
As an organization grows and matures, its need for computer resources increases. The rapid pace change in IT can also render legacy systems no longer cost-effective or obsolete. These forces make it beneficial for organizations to periodically examine their existing systems with an eye toward deploying new infrastructure with greenfield deployment opportunities.
A period of expansion, such as when expanding a factory or adding a data center, is a great time to consider the value of starting from scratch. The development and launch of a new product, the acquisition of another company and an overall digital transformation effort are also good opportunities to consider greenfield deployments.
Types of greenfield projects in IT
There are several different types of greenfield deployments. They include the following:
- Greenfield IT facility. New building projects offer an opportunity for a greenfield approach to the IT infrastructure. Instead of relying on existing network and data center designs, the facility can be completely designed to support new technologies, such as fiber optics, modular data centers, and liquid or water-cooled server room design.
- Greenfield website. As a website ages and its use grows, it becomes difficult to add new features and increase performance. Rebuilding it as a greenfield project without using any existing front-end or back-end code offers the best path forward. New technologies, such as containers, serverless computing and Jamstack, also offer improvements in performance, cost and maintainability.
- Greenfield software development. There is value in occasionally reevaluating software projects and considering the possibility of redesigning them as greenfield projects. Rebuilding can enable new programming languages, continuous integration/continuous delivery, software design and efficiency improvements. In addition, it can make software easier to maintain and modify in the future.
- Greenfield cloud expansion. New cloud computing technology offers opportunity for greenfield projects. Maintaining a hybrid IT infrastructure with both cloud and on-premises technology is often complex and difficult to maintain and troubleshoot. A greenfield cloud-first approach can provide stability and cut costs.
- Greenfield network. New networking technologies give organizations the opportunity to replace legacy networks with entirely new systems. Instead of expanding legacy Ethernet or copper-based technology, they can invest in new technology stacks, like passive optical networks and fiber optic switching. New cellular radio technology, such as 5G New Radio, enables entirely new networks to be built. Greenfield projects are often used to build new cellular networks in developing countries where there is little or no legacy technology.
Advantages of greenfield deployments
There are several advantages to doing a greenfield deployment, including the following:
- Purpose-built. Organizations can evaluate the project scope and requirements to meet the all needs of the project. They can then build custom solutions.
- Future-proof. No legacy technology means modern technology can be used for greater compatibility.
- Right-sized scaling. Project designs consider size and performance requirements, with future scaling needs built in.
- Lower maintenance. Project designs can use standards-based approaches that cut down on maintenance needs, require less institutional knowledge and enable greater employee flexibility.
- Less dependencies. Once old, outdated systems and designs are gone, new systems can be designed with greater fault tolerance.
Disadvantages of greenfield projects
Greenfield deployments aren't without their challenges. The following ones are among them:
- Slower project startup. Exploring new options and deciding which to pursue takes time; these projects are often slow in the early stages.
- Higher startup costs. New design and technology can lead to longer projects and higher costs, especially during early project phases. These are often made up for during operation through better return on investment.
- New skill requirements. IT staff that implement these systems may need to learn new skills. This takes time as employees learn to work a new system.
- New knowledge requirements. Adapting new technology often means training existing employees, bringing in new people or hiring consultants.
Greenfield deployment isn't always the right way to go. Learn more about legacy system modernization in our comprehensive guide.








