SIP trunking (Session Initiation Protocol trunking)
What is SIP trunking?
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) trunking is a service offered by a communications service provider that uses the protocol to provision voice over IP (VoIP) connectivity between an on-premises phone system and the public switched telephone network (PSTN).
SIP is used for call establishment, management and teardown. SIP trunking is typically sold as a replacement for digital Primary Rate Interfaces (PRIs), which are based on time-division multiplexing (TDM).
SIP trunking is widely deployed by communications service providers across the globe, many of which are using it to replace their TDM-based services. By delivering SIP trunking over existing Ethernet or Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) network infrastructure, the providers reduce the cost and management complexity associated with legacy digital platforms, while also provisioning additional features.
Benefits of SIP trunking
From the customer perspective, SIP trunking offers greater purchasing flexibility than TDM. TDM trunks typically support a minimum of 23 voice channels, whereas SIP trunks can be purchased in any increment without requiring a dedicated wide area network (WAN) circuit. Customers may implement SIP trunks over existing WAN services, dedicated WAN connections or even the public internet.
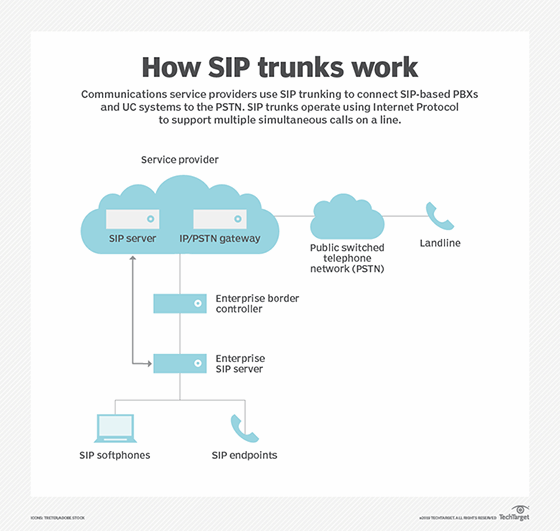
SIP trunking architecture
SIP trunking architectures typically provide for a session border controller (SBC) to mediate the connection between the SIP trunk and the on-premises phone system. SBCs provide a central point to manage security, call routing policy, numbering plans and transcoding of voice codecs.
SIP trunking providers may offer additional services, including:
- encryption of voice calls to meet security needs;
- routing of calls to 911 services, with appropriate caller location information;
- failover to backup trunks and locations;
- ability to provision trunks via a web-based interface;
- interconnection with cellular networks so a call placed to a cellphone also rings on a desktop phone;
- protection against toll fraud;
- denial-of-service (DoS) protection;
- virtual inbound phone numbers, including 800-number services;
- usage and performance reporting; and
- ability to route calls to multiple locations based on call volume, source of call or other policies.







